Whether you’re a business owner who would like to protect your sensitive information or an IT professional responsible for securing your company’s data, you need a reliable backup solution as a fail-safe to protect against unknown data disasters.
As the volume of your data increases, backups becomes necessary to maintain its integrity and ensure operational continuity. However, not all backups are equally effective, and understanding different types of backup is important for making a robust data protection plan.
In this blog, we will discuss the different types of data backups in detail to help you make the right choice for your own individual needs.
Different Types of Data Backups
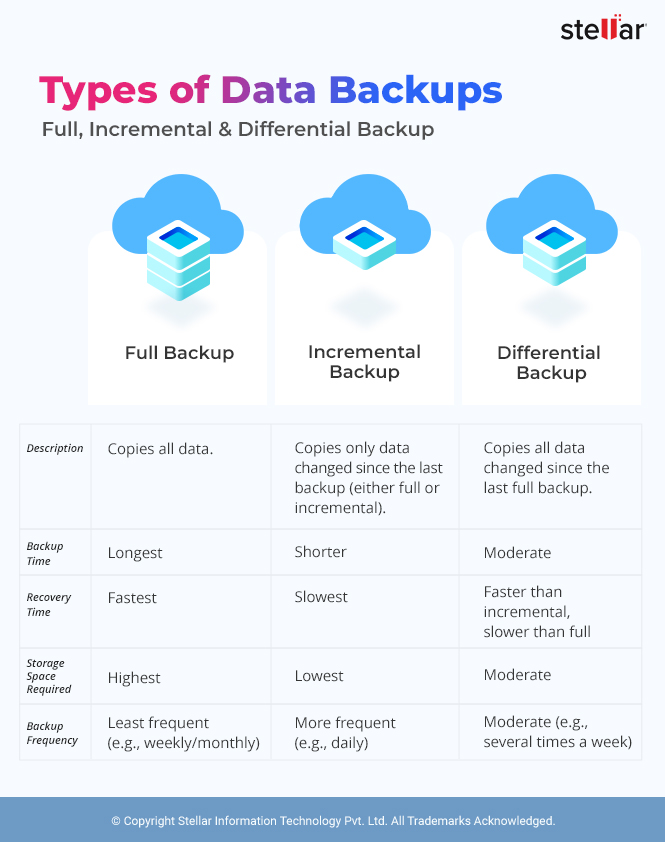
When it comes to planning your backup, you have several options. You can either back up your data manually by copying files to a different storage location, or use a backup solution that does the heavy lifting for you. Whatever your preferred method, there are three main types of backups to choose from: full, incremental, and differential.
The type of backup you choose will ultimately dictate how data is transferred from its original source to the storage location, defining your backup repository. Below, we will discuss the various backup types in detail.
1. Full Backup
A full backup involves making duplicate copies of your data, including files, directories, apps, and databases. It is one of the simplest yet most resource intensive ways of backing up your data. Full backups are suitable for those whose main objective is to reduce their Recovery Time Objective (RTO) as they keep a complete copy of your data on a single set of storage media, allowing for a swift recovery.
On the other hand, if you look at its downside, full backups take longer than other methods and require a lot of storage space. This is why these backups are performed periodically and they are ideal for users with small volume of data. To overcome these challenges, you can combine full backups with incremental and differential backups, and optimize for speed, efficiency, and security.
Pros
- Highest level of protection as they keep copies of all of your data
- Easier to restore compared to other types
- Simple storage management as data is stored in a single version
- Searching the files is easy
Cons
- Requires more storage space compared to other types of backups
- Takes a longer time to backup files
- More expensive to set up
2. Incremental Backups
As the name suggests, incremental backups only back up changes that have taken place since the last successful backup. This means a user runs a complete full backup, then follows up with a series of incremental backups that need to be done in a certain time order to reflect data changes over time. For example, if you run your full backup on the last day of the month, and then run an incremental backup on the first day of the next month, your incremental backup will only back up any modified data that has taken place since the last full backup.
This means that the system checks the modified timestamp on files changed relative to the previous backup, and the backup application logs the date and time of each change to note any changes to be backed up on the next backup. The incremental backup system allows you to take backups much faster and can take up far less storage because of the reduced data being stored, making it suitable for most users.
Pros
- Requires less storage space
- Takes less time to backup files
- Cost-effective
Cons
- Restoring data takes more time
- High risk of failed recovery
3. Differential Backup
Differential backups work similar to incremental backups by saving all the data that has changed since the previous backup. The only point of difference is that after the first run, each subsequent differential backup saves all the changes made since the first full backup. Note that this is not the case with incremental backups as they save only the changes that have occurred since the last successful backup (not all changes).
So this naturally causes differential backups to accrue more data than incremental backups, but still less than that of a full backup. And while differential backups take more time and storage space than incremental backups, they are still a more efficient way of backing up when compared to full backups. In case of a disaster recovery, you would need the last full backup and just the previous differential backup to restore your lost data.
Pros
- Faster restoration compared to incremental backups
- Require less storage space than full backups
Cons
- Require more storage space than incremental backups
- High risk of failed recovery if any of the backups files are damaged or corrupted
How to Choose the Right Type of Backup?
To choose the right type of backup method for yourself, start by assessing the criticality of your data. For highly sensitive data, you might want a full backup that guarantees the best protection and swift recovery. Other factors to consider are:
- Pay close attention to the frequency of backups required and choose accordingly.
- Carefully consider the amount of backup space required as per your individual need.
- Budget constraints should be kept in mind while planning your backup.
- Keep the recovery time in mind, as it might affect your overall Recovery Time Objective.
- To protect against cyberattacks, you can integrate your backups with immutable storage to maintain their integrity.
- Last but not least, choose a reliable data backup solution to suit your needs.
By carefully considering these factors, you can develop a backup strategy that is tailored to your specific needs and optimizes cost, security, and efficiency.