What is Recovery Pending State in SQL Server Database?
Database Recovery Pending is a state where SQL Server cannot recover the database due to MDF/LDF file corruption or insufficient disk space. When connecting to server instance after sudden system crash, reboot or restart, you may see that the state of database changed to ‘Recovery Pending’. This status means that database recovery is stuck not failed and it is not available for users.
The database goes into the Recovery Pending state when something prevents the MS SQL Server from starting the database recovery. This might happen due to resource-related issues, missing files, or problem with the database.
Let’s take a look at a user query:
| After reboot, some of my SQL Server databases randomly enter Recovery Pending state on servers running 2012R2/2016 with SQL Server 2014 SP3CU2/SP3CU3. Event Viewer shows no errors, Carbon Black Defense exemptions exist for .mdf and .ldf files. A T-SQL script temporarily fixes the issue, but recurrence is unpredictable, prompting investigation into MS SQL logs for clarity. |
What are the Reasons behind Recovery Pending State in SQL Server?
A SQL Server database may go into the Recovery Pending mode due to one or more of the below reasons:
- The database didn’t shutdown properly.
- Missing or corrupted transaction log files.
- Disk/drive, where the database is saved, is out of storage.
- Database file is corrupted or damaged.
- System is terminated or crashed abnormally.
- Bugs in MS SQL Server.
How to Check Recovery Pending State in SQL Server?
You can check the recovery pending state manually in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). When you launch it, under Object Explorer, you will see that the problematic database is showing the status as Recovery Pending, instead of SINGLE USER, ONLINE or other state.
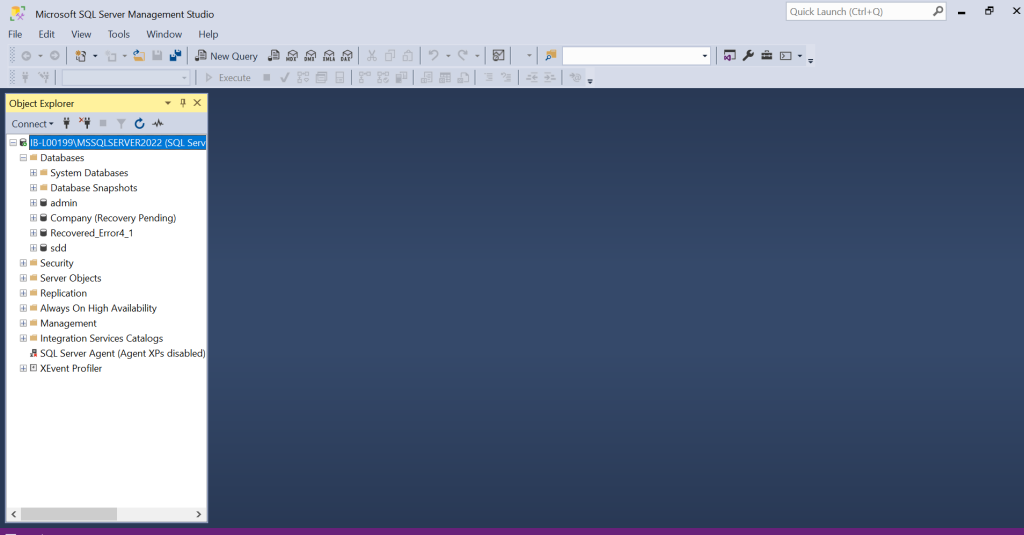
It is quite easy to check a single database state manually in SSMS. However, in production environment where a number of SQL databases are required to be managed, manually opening SSMS and clicking on each database is time-consuming.
For cases where the GUI does not provide alerts, you often require continuous monitoring of the database state – whether it is in suspect or restoring mode. In such cases, you can run the following query:
SELECT name, state_desc FROM sys.databases WHERE state_desc = ‘RECOVERY_PENDING’;

What are the Methods to Fix Recovery Pending in SQL Server Database Issue?
First, you can check the SQL Server error log. This will help you detect any issues that might be responsible for the Recovery Pending state of the database. To check the error logs, open the SSMS, expand the SQL Server Agent, and click Error Logs. If transaction log issues trigger a database state change, the error logs show it.
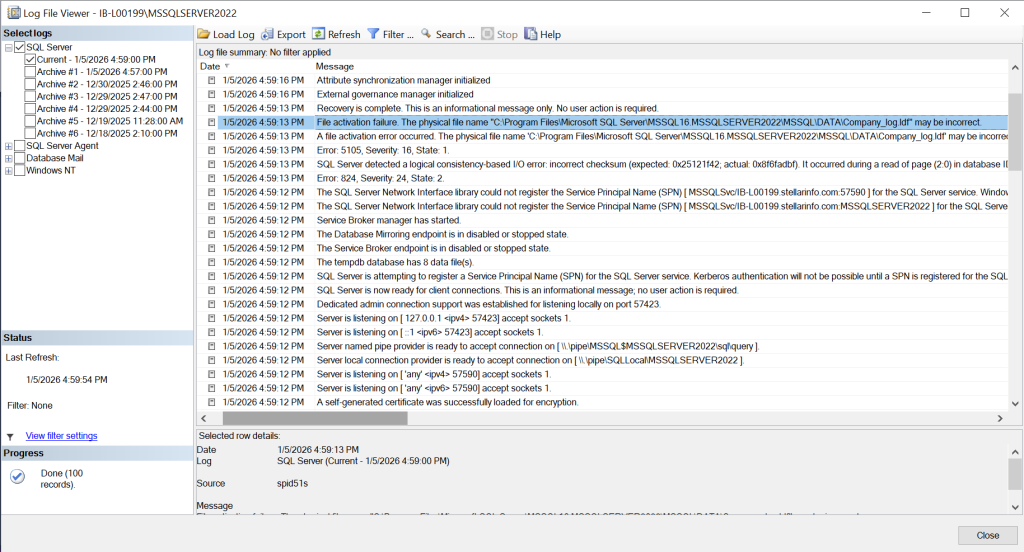
And if inaccessible, corrupted, or damaged MDF file is causing the recovery pending issue, you will see an error message (see the below image).

If you didn’t find any issues, then follow the below troubleshooting methods to bring the SQL database to normal mode.
1. Turn OFF the AUTO CLOSE Option
Sometimes, the database goes into the Recovery Pending state if the AUTO CLOSE option is ON for the database. When this option is turned ON, SQL Server repeatedly closes and reopens the database. So, if it is frequently opened and closed after each connection, it is recommended to turn OFF the AUTO CLOSE option. For this,
- Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and connect to the SQL Server instance.
- Right-click on the database and select Properties.
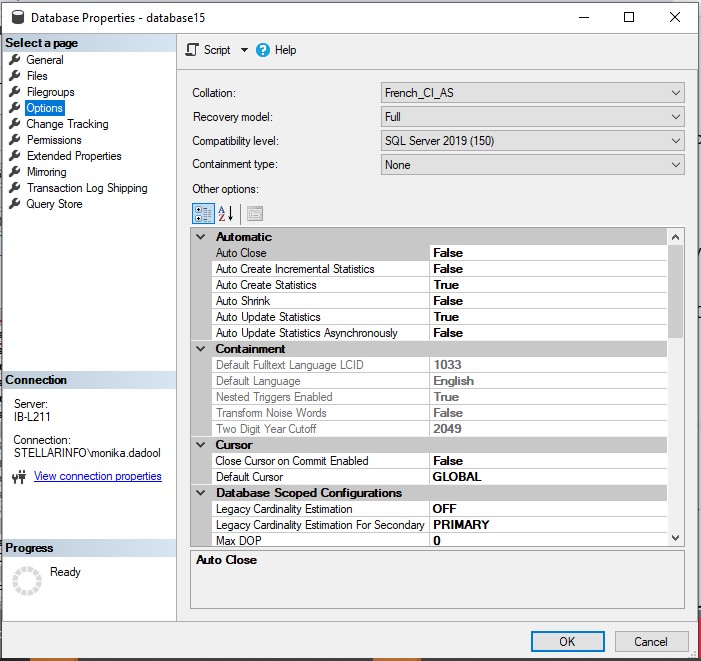
- On the Database Properties window, click on Options in the left pane.

- Under Automatic, set the value as FALSE for AUTO CLOSE and click OK to save the changes.
2. Use ALTER DATABASE Command
If SQL database server recovery pending status is due to temporary system disk issue, then you can run the following command to bring it online:
ALTER DATABASE company SET ONLINE;
If database recovery is stuck due to the I/O subsystem performance issues, like disk latency or hardware problems, then refer to this Microsoft document.
3. Recreate the Log Files
SQL database can go into Recovery Pending state if the transaction log files are missing or corrupt. You can recreate the log files by detaching and re-attaching the main database. When you detach the database (take the database offline) and then bring it online (re-attach), it rebuild the log files automatically. Here’s how to detach the SQL database:
Note: You can’t detach the database which is published, replicated, in suspect mode, or in a mirroring session.
- Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and click the New Query option.
- Set the database in EMERGENCY mode by using the below command:
ALTER DATABASE [DBName] SET EMERGENCY;
- Next, change the database to multi_user mode by using the below command:
ALTER DATABASE [DBName] set multi_user
- Now, run the below command to detach the database:
EXEC sp_detach_db‘[DBName]’
Once the database is detached, run the below command to reattach the SQL database:
EXEC sp_attach_single_file_db @DBName = ‘[DBName]’, @physname = N'[mdf path]’
Alternatively, you can attach a SQL database without transaction log file by following the steps given below:
- Open the SSMS. Connect to the SQL Server instance in Object Explorer, right-click on the Databases, and then click Attach.
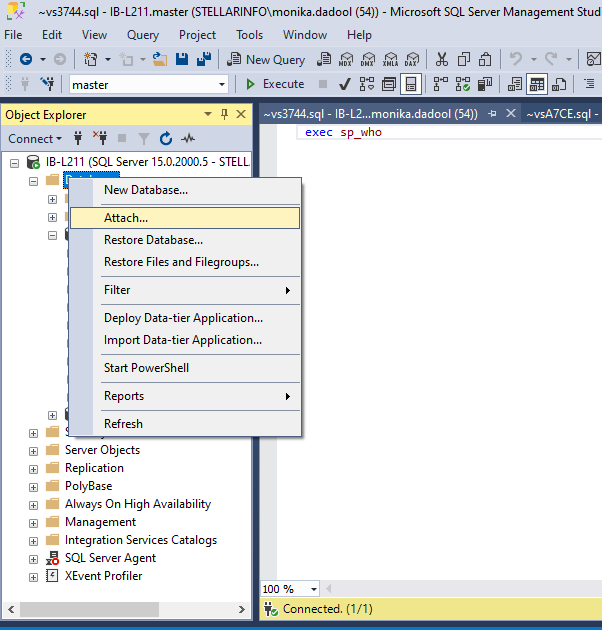
- In the Attach Databases dialog box, select the database you want to attach and click Add.
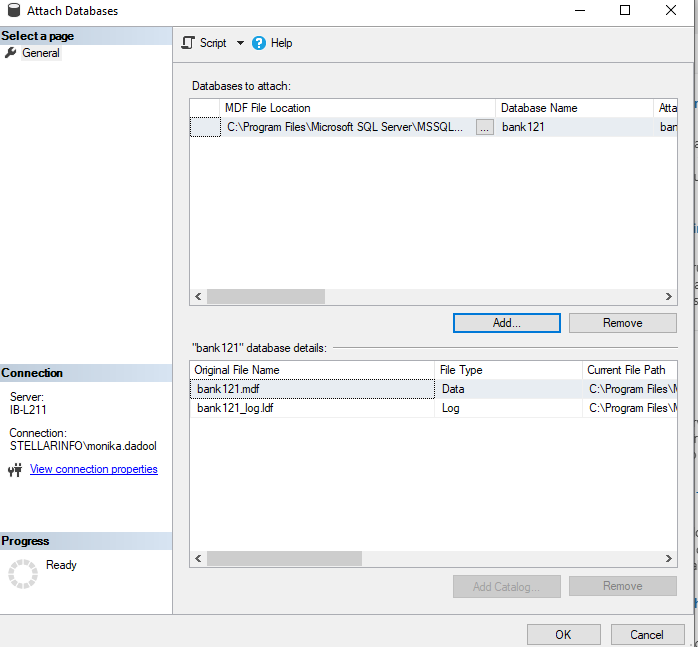
- In the Locate Database Files dialog box, select the database location and expand the directory tree to select the .mdf file. Then, click OK.
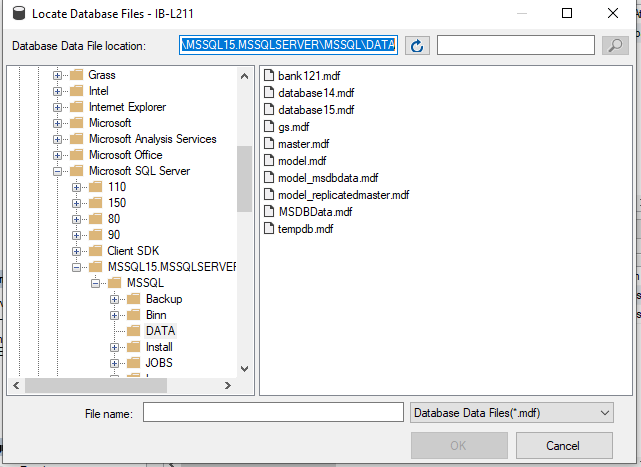
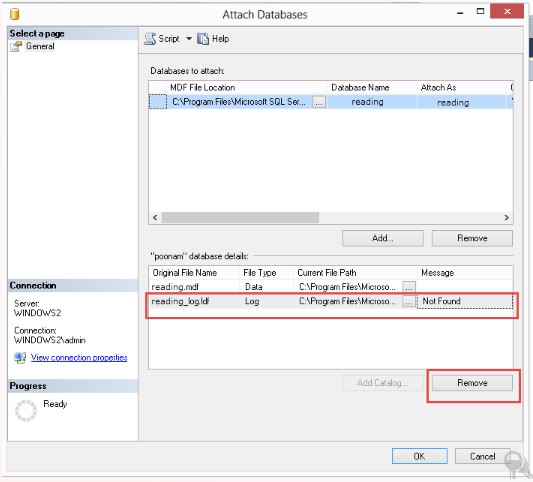
- If the transaction log file is missing, you will see the “log file not found” message in the Attach Databases window. To attach the database without the transaction log file, you need to select the transaction log file you see in the snippet and then click the Remove option. Click OK.
This will attach the database. Once the database is attached, SQL Server automatically recreates a new transaction log file in the same directory as the MDF file. And the database status will change from Recovery pending to online.
But this method has some downsides, such as:
- The uncommitted transactions will be lost.
- It requires readable MDF file.
- It requires you to detach the database, which can cause downtime. So, you can use this method when downtime and data loss is acceptable. Especially in planned maintenance process.
In case you don’t want to detach the database, then you can use the following T-SQL commands to recreate the transaction log file:
USE master;
GO
ALTER DATABASE [Company]
SET EMERGENCY;
GO
ALTER DATABASE [Company]
SET SINGLE_USER;
GO
ALTER DATABASE [Company] REBUILD LOG ON
(NAME = Company_log,
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL16.MSSQLSERVER2022\MSSQL\DATA\Company_log.ldf');
GO
ALTER DATABASE [Company]
SET MULTI_USER;
GO
4. Repair the Database
SQL Server may fail to start the database recovery if there is corruption in database (MDF/NDF) files. You can check the database for any inconsistencies or errors by running the below command with NO_INFOMSGS:
DBCC CHECKDB(Company) with NO_INFOMSGS;
The above command will display the consistency errors (if any) in the database and recommend the repair options. If it shows any issues in the database, then you need to repair the database.
If the backup file is ready to use, you can first try to restore the database from backup. If it is not available, then you can repair the database by using the DBCC CHECKDB command. Here’s how:
Note: Before initiating the repair procedure, make sure to take a backup of the database.
- Set the database in EMERGENCY mode by using the below command:
ALTER DATABASE [Company] SET EMERGENCY;
GO
- Then, execute the below command to set the database to SINGLE USER mode.
ALTER DATABASE [Company] set single_user
GO
- Now, run the DBCC CHECKDB command with the ‘REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS’ option (as given below) to repair the database.
DBCC CHECKDB ([Company], REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS) WITH ALL_ERRORMSGS;
GO
- When the repair process is finished, change the database to multi-user mode again by running the below command:
ALTER DATABASE [Company] set multi_user
GO
Limitations of using DBCC CHECKDB Command:
- It may delete damaged pages or transactions in the SQL database.
- Recovery may fail if corruption is severe.
- While executing this command, you have to prevent other users from doing changes to the database until the command completes the process.
- Fails to recover database which contains non-clustered indexes.
An Alternative Solution to Repair SQL Database
To overcome the limitations of DBCC CHECKDB command and quickly repair the corrupt database, you can use an advanced SQL database repair software, like Stellar Repair for MS SQL. It is a specialized tool that can repair severely corrupt database without file size restrictions. It can recover all the data from corrupted MDF/NDF files including non-clustered indexes with complete integrity and precision. It helps bring the database back online from the Recovery Pending state with no data loss.
Steps to use Stellar Repair for MS SQL to recover corrupt database from pending state:
- Download, install, and run the software.
- From the Select Database window, click Browse or Search to select the database file you want to repair.
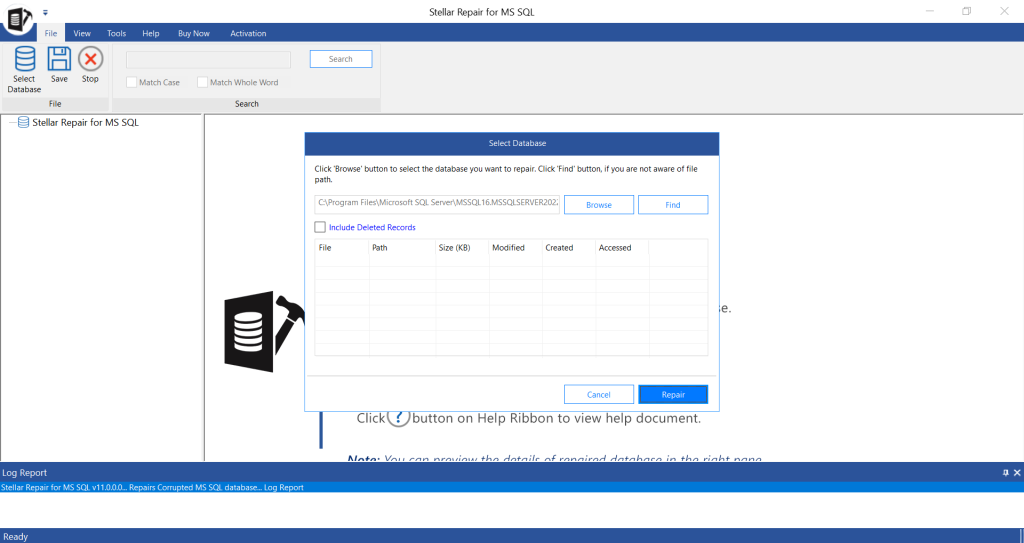
- In Select Scan mode, you will see two options – Standard Scan and Advanced Scan – to scan the corrupt database. Select the Standard Scan mode. If the database file is highly corrupted, then click on Advanced Scan. Click OK.

- On Repair Complete message box, click OK.
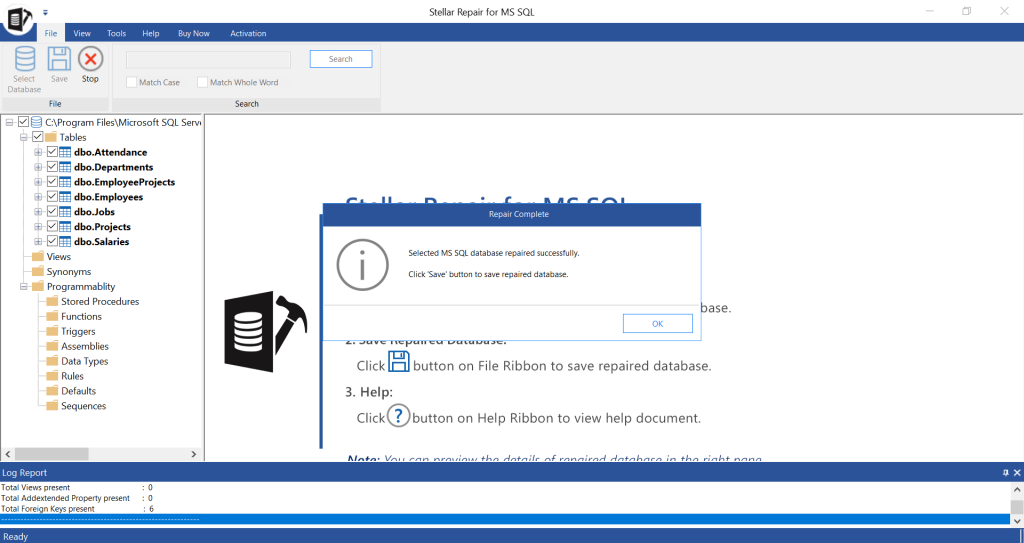
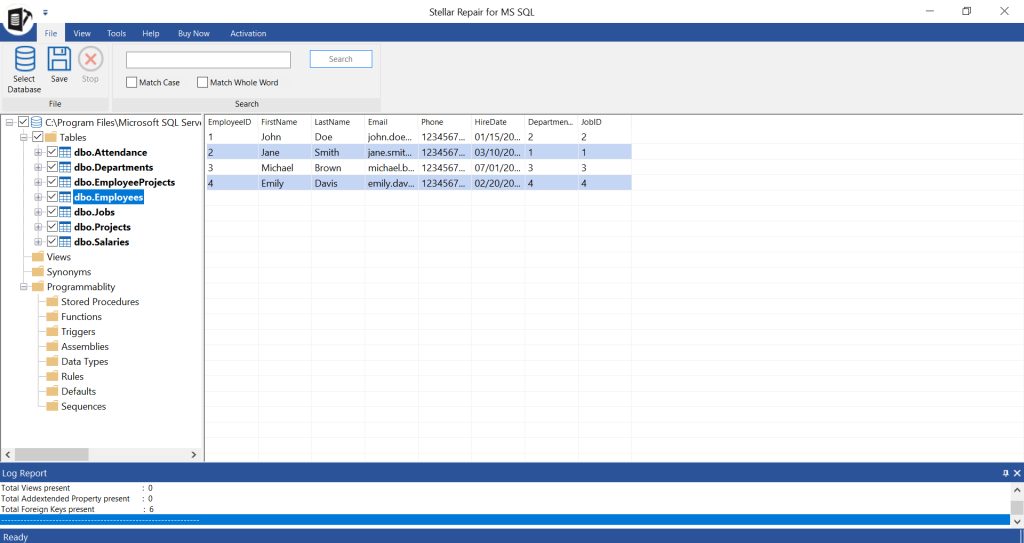
- The tool will show all the recoverable items in the database.
- To save the repaired file and its components, click Save on the File menu.
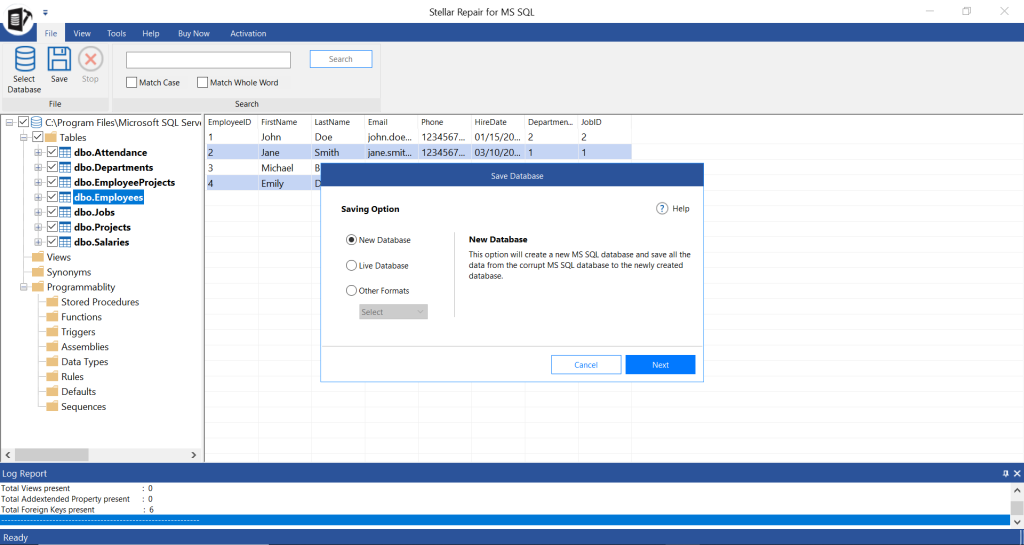
- On the Save Database window, you can select New Database, Live Database, or other formats. Click Next.
- In Save Database window, enter the required details in the Connect To Server section and click Next.
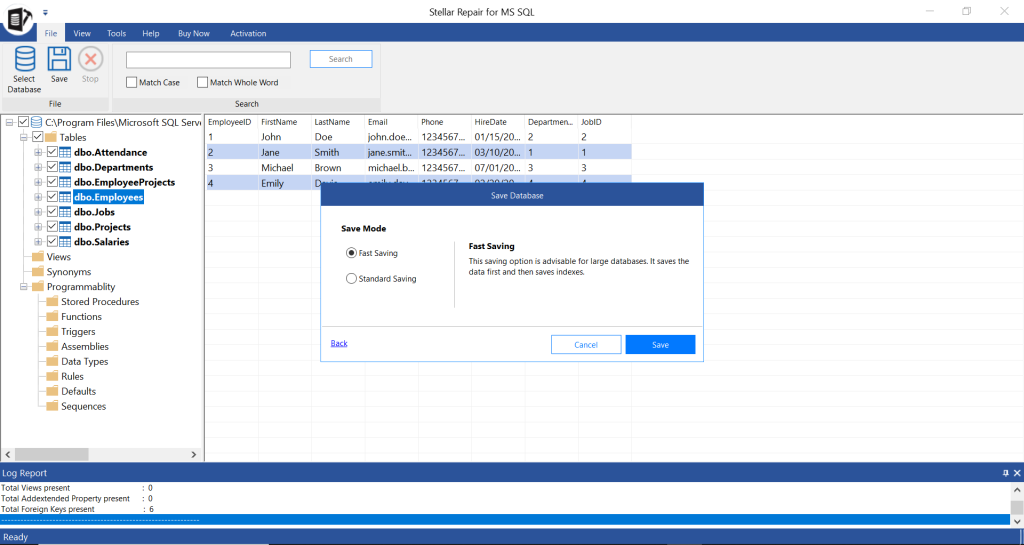
- Select the saving mode and then click Save.
- Once the database is repaired, open the SSMS and go to recovered_company under Object Explorer.
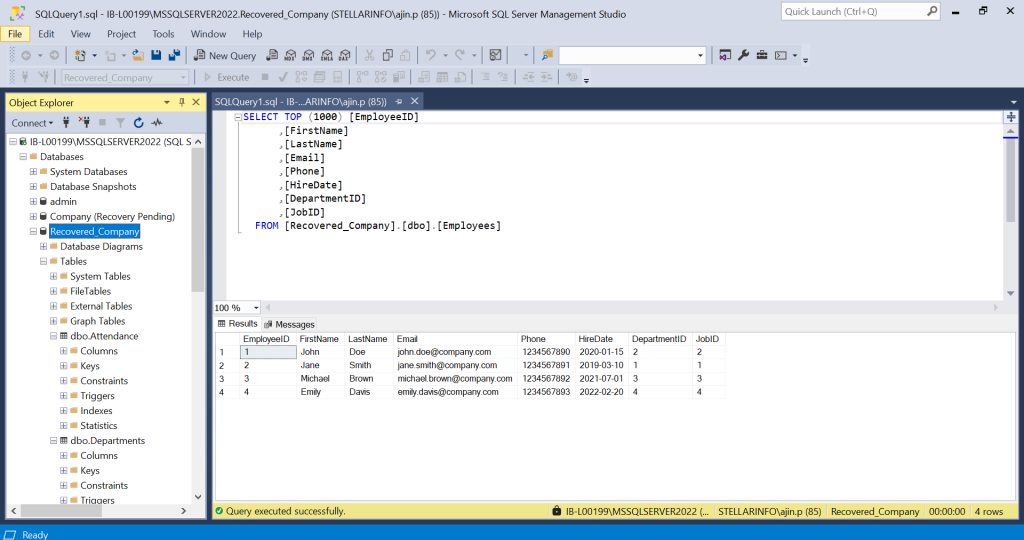
Watch this video to learn the process of recovering a SQL Server database stuck in recovery pending state issue using Stellar Repair for MS SQL.
Conclusion
SQL database can go into Recovery Pending state due to several reasons. In this post, we’ve explained how to fix the Recovery Pending state and bring the database back online. If the Recovery Pending mode of the database is due to corruption, then you can use Stellar Repair for MS SQL software to repair the database. It can repair the database (MDF/NDF) file and restore all the objects with complete integrity. It can also help you fix several corruption-related errors in SQL database.