In MS SQL Server, stored procedure is a group of T-SQL queries or references that you can save and reuse repeatedly to perform the operations effectively. It is a database object that helps to perform common database operations and automate complex tasks.
If you want to get the information related the stored procedures, then you can run the sys.procedures query as given below.
SELECT
name,
object_id
FROM sys.procedures
You can also use metadata functions to get this information.
SELECT
ROUTINE_NAME
FROM
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES
WHERE
ROUTINE_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE';
Sometimes, you face a situation where you fail to execute the queries related to stored procedures in MS SQL Server. This usually happens if there are inconsistencies or corruption in the stored procedures or the database. Below, we will discuss how to repair and recover stored procedures in MS SQL.
Causes of Corruption in Stored Procedure or SQL Database
Some common causes for corruption in stored procedure or SQL database are:
- The page in the SQL database where the stored procedure is saved is corrupted.
- Bad sectors on the system hard drive where the database is located.
- The SQL database is detached/attached suddenly.
- The system is shut down unexpectedly while altering a stored procedure.
- Bugs in MS SQL Server.
- Malware infection in the system hosting the database.
- Sudden restart of MS SQL Server instance.
Solutions to Recover and Repair Corrupt Stored Procedures in the MS SQL Server
Here are some solutions and troubleshooting methods you can follow to repair corrupt stored procedures in MS SQL Server.
Method 1: Recompile or Recreate the Stored Procedures
If there are integrity or metadata issues in stored procedures, then you can recompile or recreate the stored procedures to resolve the issue. Here’s how:
- Open the SSMS and then connect to the SQL Server instance.
- Click New Query. Then, run the command as given below:
SQL
USE AdventureWorks2022;
GO
EXECUTE HumanResources.uspProductByVendor WITH RECOMPILE;
GO
Another option you can try is to alter the procedure. For this, you can use the following code:
ALTER PROCEDURE HumanResources.uspProductByVendor
@VendorID int
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT ProductID, Name, ProductNumber
FROM Production.Product
WHERE VendorID = @VendorID;
END
If compiling and altering stored procedures, fails to work, then you can drop and recreate the stored procedure by using the following Transact-SQL command:
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS HumanResources.uspProductByVendor;
GO
Alternatively, you can delete the stored procedures and create the new ones. For this, open the SSMS and follow the below instructions:
- Open the Object Explorer and go to the Databases node
- Select Database > Programmability.
- Select Stored Procedures and then right-click on the stored procedure you want to delete.
- Select the Delete option.
Now, you can create new stored procedures.
Method 2: Restore the Backup File
When there is corruption in database objects, like stored procedures, etc., then you can try to restore the database from the backup. Follow the below-given step to restore the backup file:
- Launch the SSMS and connect to the SQL Server instance. Click on New Query.
- The Query Editor window is displayed. Enter the following command for restoring the complete database from the backup:
USE[master];
GO
BACKUP DATABASE [Stellartestbackup]
TO DISK = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\Stellartestbackup.bak'
WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT,
NAME = N'Stellartestbackup-Full Database Backup', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10;
GO
You can also use the graphical user interface of SSMS to restore the database from the backup (.BAK) file.
Method 3: Repair Database using DBCC CHECKDB Command
If the backup file is obsolete, damaged, or inaccessible, then you can repair the SQL database using the DBCC CHECKDB command. This command helps fix issues or errors caused by corruption in the database. Before repairing the database, change the database to SINGLE_USER mode. Follow the given steps:
- In SSMS, connect and expand the instance of the SQL Server Database Engine in Object Explorer.
- Right-click on the database and then click Properties.
- In the Properties window, click the Options page.
- On the Options page, scroll down and click Restrict Access > Single_user > OK.
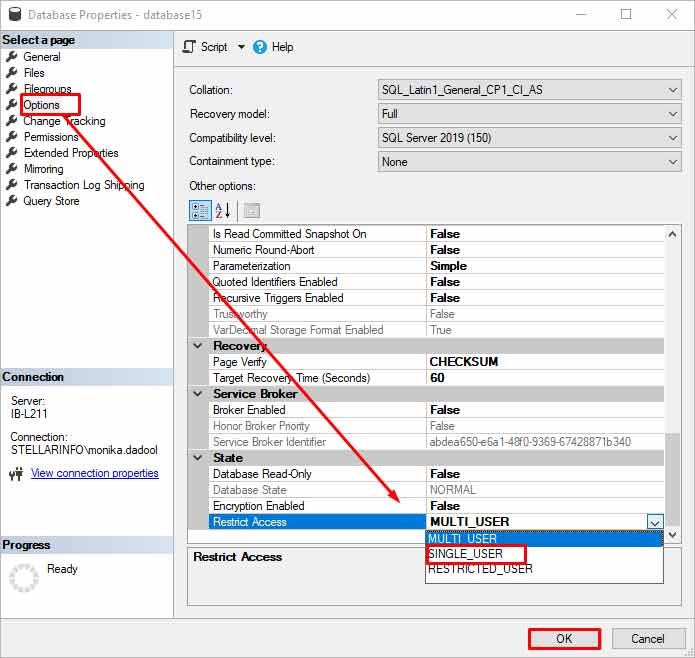
Once you’ve changed the database mode to single user, click on Next Query in the SSMS. Then, run the DBCC CHECKDB command with REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option to repair the database (see the below example).
DBCC CHECKDB (N ’Dbtesting’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS) WITH ALL_ERRORMSGS, NO_INFOMSGS;
GO
After repairing the database, you need to change the database mode from SINGLE_USER to MULTI_USER.
Method 4: Repair Corrupt Database using an Advanced SQL Repair Tool
To repair and restore corrupt stored procedures and other objects from SQL database, you can use Stellar Repair for MS SQL. This dedicated SQL repair tool can efficiently repair SQL database (both MDF and NDF) files with complete precision and consistency. It recovers all the objects, including stored procedures and tables, from the database and saves them in a new healthy file. This MVPs-recommended SQL repair tool supports databases created in MS SQL Server 2022, MS SQL Server 2019, and all earlier versions.
Conclusion
If the stored procedures get corrupted, you can face data integrity issues in the SQL database. To fix the issue, you can recompile the stored procedure or use the DBCC CHECKDB command to repair the entire database as explained in this article. However, there are chances of data loss when you repair the database using the DBCC CHECKDB command with the REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option. The best solution is to use Stellar Repair for MS SQL. It can quickly repair SQL databases and recover all its objects with absolute precision and integrity. It can even recover deleted records from the database. The tool has an intuitive interface that makes the repairing process quite easy and convenient.