Which type of image compression format is best?’
‘Why is my camera not saving uncompressed photos anymore?’
This blog answers all such questions like which image compression is right for you – Lossless Compressed vs. Lossy Compressed vs. Uncompressed? But before all that, let’s understand ‘what is compression’ and ‘what does it do to your images’.
What is Compression in Photos?
Compression, as the word suggests, reduces size and quality of your photos. It reduces finer details of color, contrast, and sharpness from your images.
You can compress images either in your camera by adjusting settings through the menu or on your computer by using a photo editing or photo viewing software.
Since compression compromises on the file size and quality, photographers are often weary of it.
Compressed image format
Compressed images are referred to when the file space of the image is reduced by eliminating or rearranging certain pixels of the original image. The compressed images are of a relatively smaller size, making it easy to store, transmit, or upload them. There are two types of compressed images:
- Lossless compression
- Lossy compression
Uncompressed image format
Uncompressed images (i.e., RAW format) have all the details exactly as captured by the camera sensor. This is why the uncompressed RAW format photos are of high quality and large size.
Professionals prefer the uncompressed RAW files. They get creative leverage by playing with aspects such as brightness, color, sharpness, white balance, noise reduction, etc. On the other hand, the biggest disadvantage of uncompressed images is that they consume a large amount of storage space. After shooting in uncompressed RAW format, you’re able to store fewer photos on your camera card.
Every camera has its special RAW file type, such as NEF in Nikon, CR2 in Canon, RAF in Fuji, etc. Further, the camera lets you record RAW photos in different compression formats per your needs. You shall get options like uncompressed, lossy compressed, or lossless compressed in your camera. These compression options for the RAW file are known to differ from one model type to the other and from one brand to the next.
For example, in Nikon cameras, there are three options available when it comes to JPEG compression, including Compressed, Lossless Compressed, and Uncompressed. In Sony cameras, there are only two options available when it comes to compressed RAW files, including Compressed & Uncompressed.
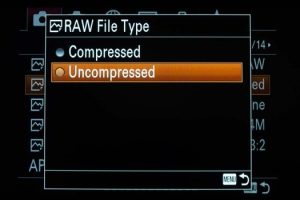
RAW Compression options in Nikon D850
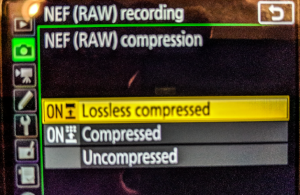
RAW Compression options in Sonya7III
Compressed Vs. Uncompressed Images
| Feature |
Compressed (Lossy or Losseless) Images |
Uncompressed Images |
| File Size |
Small |
Very large |
| Image Quality |
Good but lower over time (lossless) or slightly reduced (lossy) |
Maximum |
| Editing Flexibility |
Limited |
High |
| Performance |
Fast loading |
Takes time to open or load |
| Compatibility |
Works with all software |
Special software is needed |
| Best Use |
Use this format for website and apps, or for sharing |
Editing, printing, or archiving |
Why should one compress their images?
The biggest benefit of compression is that it reduces the file size, hence letting you save a larger number of images in a drive or camera SD card.
- But this advantage is accompanied by a sacrifice in the photo quality. Other than this, if you face a photo quality issue due to image corruption or over compression, you can use Stellar Repair for Photo to fix your photos
So, which image compression format is right for you? To get the answers, first know the difference between the two types of compression:
Lossless compression
Lossless Compression indicates that images are being compressed without losing data. This indicates that it is possible to compress images to achieve small sizes without losing much on their quality. This is similar to archiving the files into Zip.
Lossless compression is preferred to save RAW files while preserving image data. The images saved in this format occupy less space. Although there is a little loss in quality of the images that is not visible to the eyes.
When lossless compressed images are edited using an editing program, decompression of pictures takes place.
Therefore, it can be said that lossless compression techniques are efficient methods to be used in storing RAW photo file formats of a camera. TIFF, GIF, PNG, and BMP images come under the category of lossless images.
Lossy compression or compressed format
If the image is compressed by losing some of the data from the picture, the process is known as lossy compression. The main point of difference in lossless compression is that the images are decompressed in the processing software before the photos are compressed by the lossy compression method. Once the lossy compression method is used for an image, it cannot be decompressed.
Since lossy compression compromises the image data, it limits the post-processing process. Thus, professional photographers don’t favor image compression.
In fact, some cameras, such as Sony’s, shoot RAW photos in lossy compression by default, which is widely criticized by the photography community. Like Nikon, Canon etc., Sony doesn’t have the option for lossless compression.
Nonetheless, you may choose lossy compression to save thousands of photos on an SD card, as it significantly reduces the size of the image file.
Difference Between Lossy and Lossless Compression
| Feature |
Lossy Compression |
Lossless Compression |
| Data Removal |
Yes, some data is removed permanently. |
No, data is removed while saving the image using lossless compression |
| Image Quality |
Slightly reduced |
Original image quality is preserved. |
| File Size |
Very small |
Larger |
| Reversible? |
No, once the image is saved using lossy compression, the removed data is gone forever. |
Yes, you can decompress the image to restore it to its original state with no quality loss. |
| Best For |
Websites, blogs, e-commerce product images, and social media uploads. |
Logos, icons, UI elements, professional editing, etc. |
Which Compression Is Right For You – Lossless, Lossy, Or Uncompressed?
Choosing the correct compression purely depends on how you are going to use the photos.
For creative liberty
Professional photographers who desire images of high quality and creative freedom in the editing stage, are likely to use an uncompressed or lossless compressed RAW format. As stated earlier, it can give them great latitude to work on their photos.
To print photos
If you want to print photos, a high-resolution image with at least 300 pixels of information is advisable. Lossless compression, in which the original image data is intact, is suitable for printing.
To upload an image online
For uploading images online, for example, on Instagram or Facebook, a lossy compressed image format with a smaller file size is apt. You may use JPEG, PNG, or GIF to upload photos online.
To publish on the web
To publish an image on a website, download speed is crucial. The uncompressed and lossless compressed RAW formats won’t help, as they would make your webpage extremely slow to load.
To use high-quality images that don’t slow your website, you have to optimize image compression. Image optimization helps to get the desired compression while maintaining image quality and reducing the page load time on your web page.
WordPress plugins, such as Optimole, reSmush.it, Imagify are available that can help you optimize the compression of photos for the web. Other ways to optimize images are by using image editing software such as Photoshop.
Image Compression Tips
- Shoot in RAW uncompressed or lossless compressed.
- Convert RAW format to a lossless file format to reduce file size.
- Opt for image optimization for greater control over quality and compression
- Use high-class and capacity SD cards to overcome space constraints
- Don’t save over lossy compression file format (JPEG) as it leads to further quality loss
- Use Stellar Repair for Photo to repair corrupt compressed or uncompressed RAW photos
- Use JPEG compression for sharing images
Wrapping Up
Compression of images in a camera or computer reduces the details of color, sharpness, and contrast present in the original picture. Thus, you compromise on image quality when applying compression. But the biggest advantage that approves compression is that it saves a lot of space on your storage card or media.
Professionals prefer the uncompressed or lossless compress RAW file format. This gives them leverage while processing or editing the pictures.
However, if it’s not your professional necessity, shooting and saving in lossy compression format, such as JPEG is convenient.