Let’s assume that the migration has already been done and the MX records have already been re-routed to Office 365. The organization has decommissioned the Exchange Server while retaining the Active Directory Server for authentication and having the client machines all joined to the Azure Active Directory. Also, a final backup is taken before the servers are decommissioned.
Before diving straight into the process of shutting down the Exchange Server and decommissioning the server’s hardware, it is important to perform a clean uninstallation. So, you need to clean off the Active Directory Schema. A manual clean-up of the schema using the ADSIEdit is highly risky as after removing or modifying the ADSIEdit, there is no undo button. If something goes wrong, you could end up with your Active Directory being unusable.
The Decommissioning Process
The process for this is as follows:
- Right-click on Start.
- Click on Run and type ADSIEdit.msc.
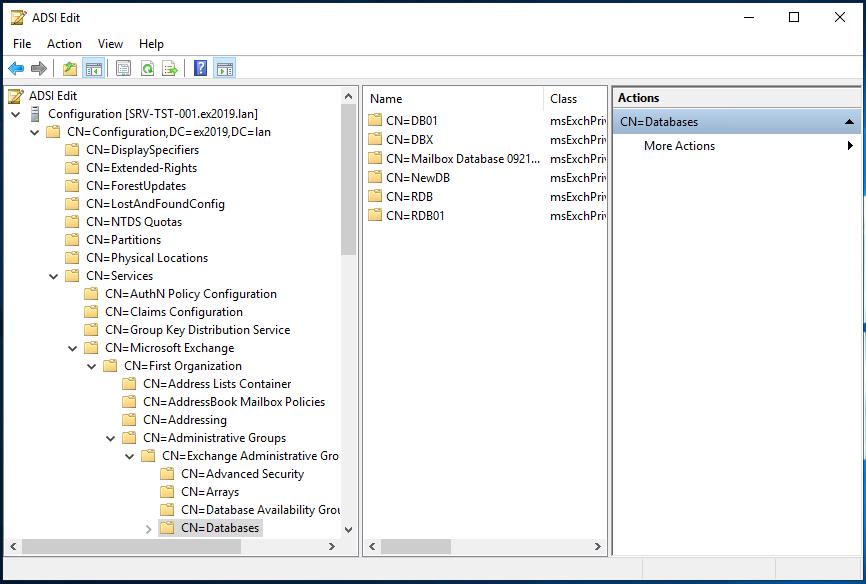
- Open Configuration/Configuration Services.
- Open Microsoft Exchange/ <Your Organization>.
- Open Administrative Groups and Exchange Administrative Groups.
- Open Databases and delete the desired databases from the list.
This could have repercussions on the stability of your Active Directory setup and the users would be unable to log into their services or machines. This would also impact applications which are Active Directory dependent.
The first step is to delete all the mailboxes from the databases. After this is complete, you need to manually remove the arbitration mailboxes. This can be done by using the below command in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
Get-Mailbox -Arbitration –Database | Disable-Mailbox –Arbitration –DisableLastArbitrationMailboxAllowed

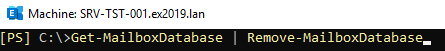
Once this is done, you can go ahead and remove the actual mailbox database from the server. For this, use the Remove-MailboxDatabase command as given below.
Get-MailboxDatabase | Remove-MailboxDatabase
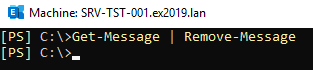
Next, you need to remove any pending messages in your Exchange Server Queue. These are the messages which are not delivered or stuck.
Get-Message | Remove-Message
The next step is to uninstall the Exchange Server from the Add remove programs. Once all is done and there are no issues, you can simply disjoin the Exchange Server from the Active Directory and decommission the hardware hosting the Exchange Server.
In case of a hybrid setup, before you go ahead and uninstall the Exchange Server, you need to first remove the hybrid configuration of the local setup. For this, use the following command.
Remove-HybridConfiguration -Confirm:$false
Then, you need to remove the connectors from your Exchange Online from the mail flow and Connectors section.
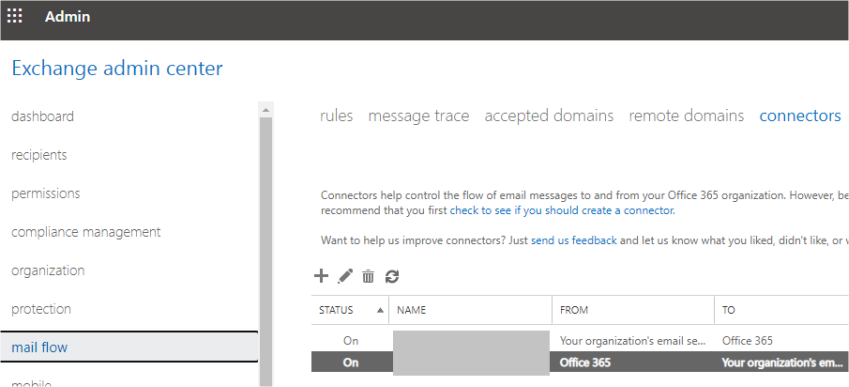
Also, the Organizational Sharing from the organization and sharing section.
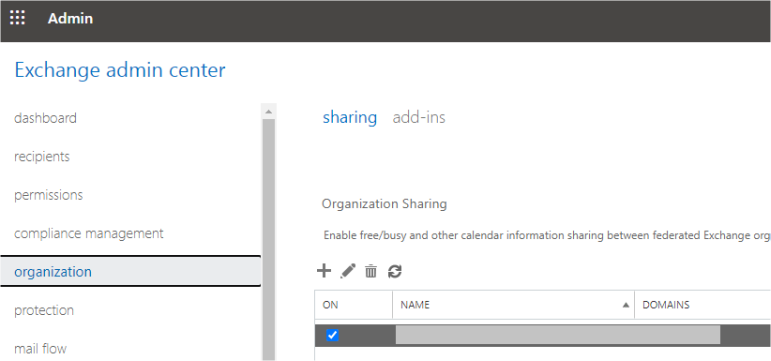
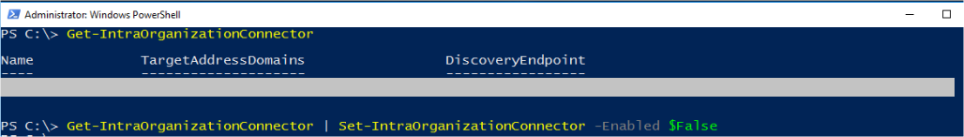
Lastly, disable OAuth on-premises using the command below on both the local Exchange Server and Exchange Online.
Get-IntraorganizationConnector | Set-IntraOrganizationConnector -Enabled $False
Note: Microsoft recommends to not remove the Exchange Hybrid option in the Azure AD Connect.
What Could go Wrong?
You may either miss resources or encounter an issue or lost some data in the transition. It is a very difficult task to restore the whole server, especially after migrating from on-premises to Office 365 and decommissioning the Exchange Server. If the Active Directory is retained, the Exchange Server is decommissioned, and the Active Directory schema is cleaned up, restoring the Exchange Server alone would not be sufficient as you will end up with the mailbox databases that are not mounting due to requirements from the Active Directory.
You also need to consider the resources and administrative effort required to restore the whole infrastructure. In case you only backed up the databases, you will not be able to port those databases back into the new Exchange Server installation. Also, if you have decommissioned all the servers after the migration, you need to acquire new hardware.
The Solution
In such cases, Stellar Migrator for Exchange offers a more seamless and comprehensive migration and recovery solution. This tool is specifically designed to simplify the migration of mailboxes from Exchange Server directly to Office 365 or live Exchange Server environments.
It supports granular migration, allowing you to selectively migrate primary mailboxes, archives and public folders to Exchange Server or Office 365. The software also preserves mailbox structure, ensures data integrity, and supports parallel processing for faster migration.
In the absence of the original Exchange infrastructure, Stellar Migrator for Exchange helps bridge the gap by facilitating direct, reliable mailbox migrations with minimal effort and no risk of data loss.