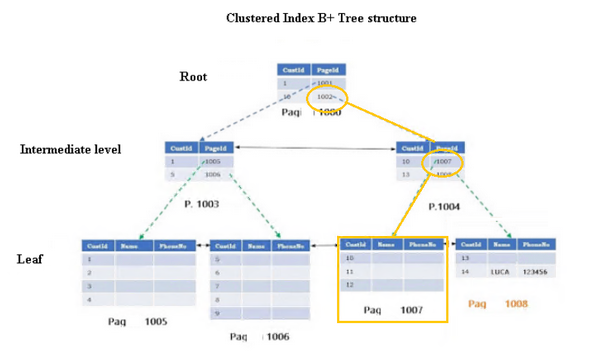
Indexes are important schema objects of MS SQL database files that enhance the data retrieving operations on a table. In simple words, these objects function like a table of contents of the database. These indexes have B-tree structure (where the letter “B” stands for balanced), which is a multilevel structure that has root, intermediate, and leaf levels. At the leaf level, a "doubly linked list" links the pages. This link is used to scan an index.
There are two types of indexes in SQL Server – clustered and non-clustered. A clustered index physically stores the data within the table, defining the logical order of table. On the other hand, a non-clustered index stores data separately from the table. It has a similar B-tree structure but points to the clustered index for its data.
Over time, continuous INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations can fragment the database tables. When fragmentation increases, query performance degrades, and data concurrency and locks increase. Also, the server may choose not to use a fragmented index.
Indexes are also prone to corruption. If the indexes get corrupted, you can receive errors. Some common errors are:
Table error: table 'Items' (ID 1954106002). Data row does not have a matching index row in the index 'IX_Advertise_BrandCopy_Price_Stock' (ID 69). Possible missing or invalid keys for the index row matching.
Msg 8955, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Data row (1:11226494:9) identified by (Id = 11078215) with index values 'AdvertiseFlag = 1 and BrandCopyParentId = 0 and NSFPPrice = 137.50 and NSFPQtyInStock = 0 and Id = 11078215'.
Msg 8951, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
In case of high fragmentation or corruption in indexes, you can reorganize or rebuild the indexes to resolve the issue. In this article, we will discuss how to reorganize and rebuild the indexes in SQL Server. But before proceeding, let’s understand more about fragmentation.
What is Index Fragmentation?
Fragmentation is a natural phenomenon that happens in a database over time, when rows are continuously inserted, updated, and deleted. It is defined as a condition when data pages are not stored contiguously. In a B-tree index, fragmentation usually occurs when pages, where the logical ordering (within the index, based on the key values of the index), do not match the physical ordering of the index pages.
For example, when rows are added to a page in a table but there is not enough space, SQL Server database engine automatically splits the page and moves some data to a new page. This process modifies the indexes, which in turn impact the data continuity and order. However, SQL Server updates the pointer on the both pages (original and new) to maintain the logical sorting order in the index. But it still leads to fragmentation.
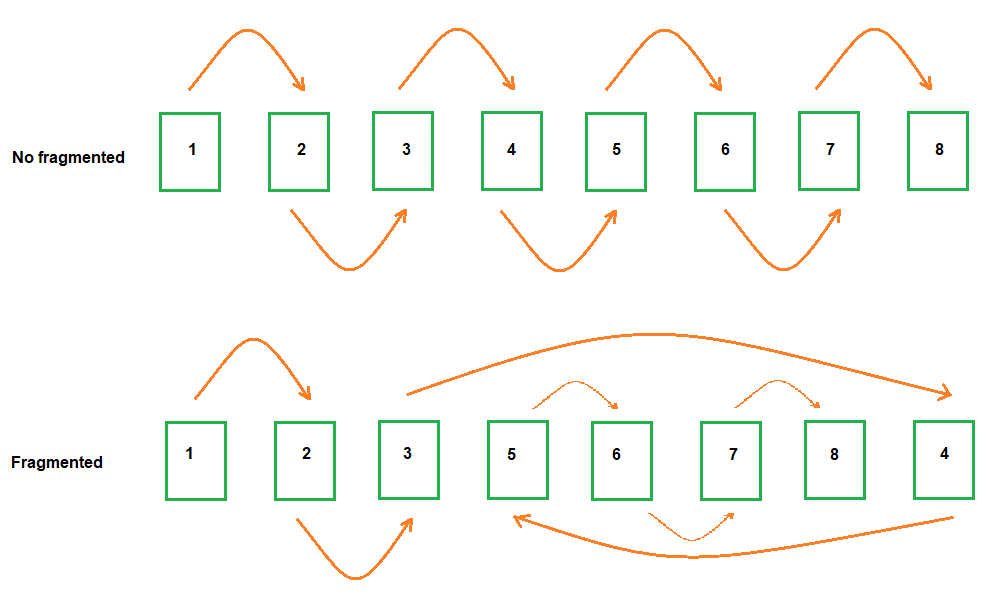
Types of Index Fragmentation
There are two types of index fragmentation:
- Logical Fragmentation - When the logical order of the pages does not match the physical order. From a performance standpoint, logical fragmentation leads to an increase in the number of physical reads.
- Internal Fragmentation - When data pages in the index contain free space. Internal fragmentation leads to an increase in logical reads.
How to Detect Index Fragmentation or Determine the Degree of Fragmentation?
You can identify fragmentation in a specific index or all indexes defined on a table or in a database using the Dynamic Management Function (DMF) - “sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats.”
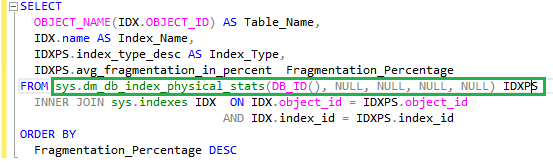
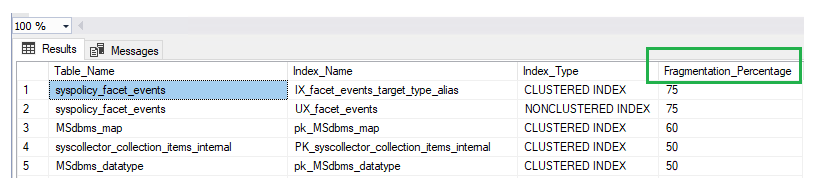
According to Microsoft, if the fragmentation is less than 5%, there is no need for defragmentation. If the fragmentation is between 5% and 30%, you should reorganize the indexes. If the fragmentation is greater than 30%, you need to rebuild the indexes.
After getting the fragmentation percentage, you can choose the best method to defragment the indexes. You can rebuild/reorganize indexes using the SQL commands, SSMS, and maintenance plans. Let’s discuss these in detail.
How to Reorganize Indexes in SQL Server?
Reorganizing the index improves its structure by moving the pages into a more efficient search order. It also helps the index rows to deallocate unused pages. Swap the remaining pages in small transactions until all the pages are in logical order. The result will produce logically ordered pages rather than physically contiguous pages. To reorganize the indexes, you can follow the below methods:
1. Reorganize Indexes using T-SQL Command
You can reorganize the index using the below T-SQL command.
ALTER INDEX IDX_Ordtes_Datedoc
ON Ordtes
REORGANIZE
GO
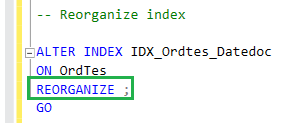
In the above command, OrdTes is the table, with the index - IDX_OrdTes_DateDoc.
2. Reorganize the Indexes using the SSMS
You can also reorganize the indexes using the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Follow the below steps:
- Open the SSMS. In Object Explorer, expand the database that contains the table on which you want to reorganize the indexes.
- Expand the Tables folder.
- Expand the table on which you want to reorganize the indexes.
- Right-click the Indexes folder and select Reorganize All.
- In the Reorganize Indexes dialog box, verify the indexes to be reorganized. To remove an index from the Indexes to be reorganized grid, select the index and then press the Delete key.
- Select the Compact large object column data checkbox to specify that all pages that contain large object (LOB) data are also compacted.
- Click OK.
3. Reorganize Index in a Maintenance Plan
You can also reorganize the index in a maintenance plan. SQL Server offers an option to schedule a maintenance plan that periodically carries out this activity. The maintenance plan will not only defragment the index but also allow you to perform other important operations, such as statistic maintenance and database backup.
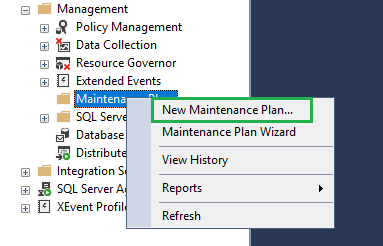
To create a new maintenance plan, right-click on the maintenance item from the Management menu. Then, select the New Maintenance Plan option.
In the maintenance plan, you can add various tasks. To perform the Reorganize Index Task, drag and drop the Reorganize index task to the center of the screen. 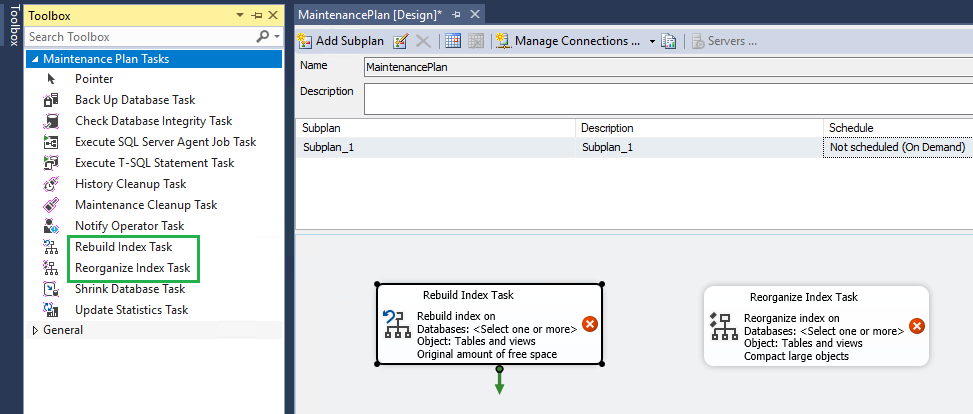
Once you have added one, you should set it. To set up the Reorganize Index Task,
- Specify on which databases that operation needs to be performed.
- Choose to reorganize only the necessary databases, the user databases, or the system databases.
- Choose to Reorganize the indexes only under certain conditions, such as above a certain percentage of fragmentation or above a certain number of pages.

How to Rebuild Indexes in SQL Server Database?
The process of rebuilding indexes is different in comparison to reorganizing the indexes. This process builds a new index from scratch and drops the old one. This happens regardless of the fragmentation present in the older index. It requires enough space to build a new index.
You can perform rebuilding of indexes online or offline. The terms Online and Offline indicate whether the index can be kept accessible during the rebuild operation. The Standard version of MS SQL Server supports only the Offline type, while the Enterprise and Developer versions also support the Online type. Let’s see the ways to rebuild the indexes in SQL Server.
1. Rebuild Indexes using the T-SQL Command
If the fragmentation is higher, then you can rebuild the indexes. You can use the DBCC DBREINDEX command to rebuild an index. Here’s how to execute this command:
DBCC DBREINDEX
(
table_name
[ , index_name [ , fillfactor ] ]
)
[ WITH NO_INFOMSGS ]
This command does not support spatial indexes and memory-optimized column store indexes.
Alternatively, you can use the ALTER INDEX command as given below:
ALTER INDEX [PK_Person_BusinessEntityID] ON [Person].[Person]
REBUILD;
2. Rebuild the Indexes using SSMS
You can use the graphical user interface of the SQL Server Management Studio to rebuild the indexes. Here are the steps:
- Open SSMS and go Object Explorer. Expand the database that contains the table on which you want to rebuild an index.
- Expand the Tables folder.
- Expand the table on which you want to rebuild an index.
- Expand the Indexes folder.
- Right-click on the index and select Rebuild.
- In the Rebuild Indexes dialog box, verify the indexes to be rebuilt and click OK.
- Select the Compact large object column data checkbox to specify that all pages that contain large object (LOB) data are also compacted.
- Click OK.

3. Rebuild Indexes in a Maintenance Plan
You can also rebuild the index in a maintenance plan. To do so, follow the below steps:
- First, create a new maintenance plan. For this, from the Management menu, right-click on the maintenance item and then select the New Maintenance Plan option.
- In the maintenance plan, drag and drop the Rebuild Index Task to the center of the screen.
- Now, you need to setup the rebuild task. For this:
- Specify on which databases that operation needs to be performed.
- Choose to reorganize only the necessary databases, the user databases, or the system databases.
- Choose to rebuild the indexes only under certain conditions, such as above a certain percentage of fragmentation or above a certain number of pages.
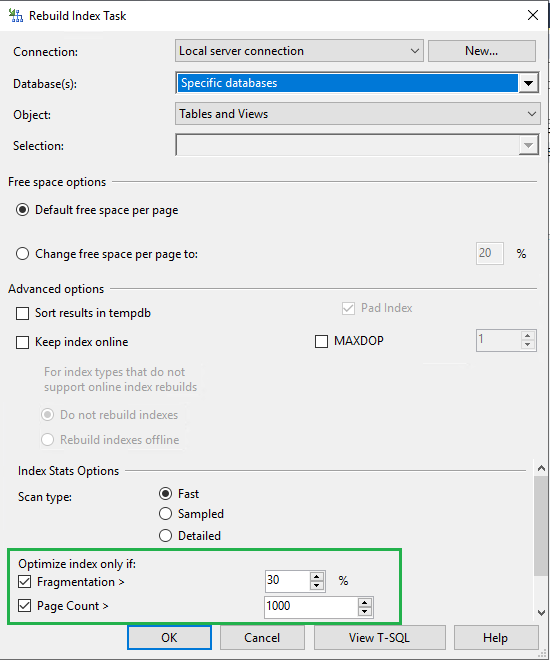
- Now, save the maintenance plan and schedule it to run at a certain frequency.
Repair the SQL Server Database
If indexes are corrupted and reorganizing or rebuilding did not help, then you can try the DBCC CHECKDB command with 'REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS' option to repair the database. Here’s how to use this command:
- First, change the mode of the database to SINGLE_USER by using the below command:
- Next, run the DBCC CHECKDB command as given below to repair the database:
DBCC CHECKDB (N ’Entity’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS) WITH ALL_ERRORMSGS, NO_INFOMSGS;
GO
- After repair, set the database mode to MULTI_USER by executing the below command:
The above DBCC CHECKDB command can help you resolve minor corruption issues in clustered and non-clustered indexes in SQL database. But it can result in data loss. To prevent data loss, you can use Stellar Repair for MS SQL - professional MS SQL repair tool that can quickly repair database (both MDF and NDF files) with complete integrity and precision. It can recover all the objects, including clustered and non-clustered indexes, triggers, pages, stored procedures, etc., from the corrupt database. It allows you to save all the data recovered from the database to a new SQL database file and in various other formats. It can help you resolve index corruption-related errors in SQL database.
To Conclude
Reorganizing or rebuilding the indexes helps you reduce fragmentation and resolve corruption. This article discussed the process to reorganize and rebuild indexes in SQL Server database. In case the reorganizing and rebuilding of indexes do not work, you can restore the database from backup or use Stellar Repair for MS SQL software. This easy-to-use software can help fix index corruption in the SQL Server database and restore the database to its original form. The software supports SQL Server 2022, 2019, 2017, and previous versions.













 7 min read
7 min read







