RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a storage technology that combines multiple hard disks to form one or more logical units. RAID is mainly designed for higher read/write speed and improved data redundancy, or both—over the traditional hard drive storage.
There are different RAID levels, such as RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, and more. The first step in setting up RAID on your home server is choosing a suitable RAID level. But with so many options available, it's not easy to choose the one which is precisely appropriate for you. In this article, we'll take a look at the factors that you can consider when choosing the RAID level for your home setup.
How to Choose the Best RAID Level for Home Server?
When choosing a RAID level, it is to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach. There are various types of RAID levels and each has different architecture and functionality. Therefore, being a home user, you need to consider your specific requirement and some specific factors when choosing the RAID level. Let's take a quick look at these factors.
Capacity
Different RAID configurations offer different amounts of usable space. As a result, the storage capacity available after accounting parity or other RAID overhead varies from one level to another.
RAID 0
- RAID 0 offers maximum capacity since it has no parity data and mirroring. You can use the entire storage capacity of the disks in the array.
RAID 1
- Only 50% capacity can be used for storage as the other half contains a mirrored copy of the data.
RAID 5
- This requires one drive capacity per RAID set. So, the usable capacity will always be one drive less than the total number of drives in the RAID configuration.
RAID 6
- The usable capacity will always be two drives less than the total number of drives in the RAID configuration as it uses striping with dual parity.
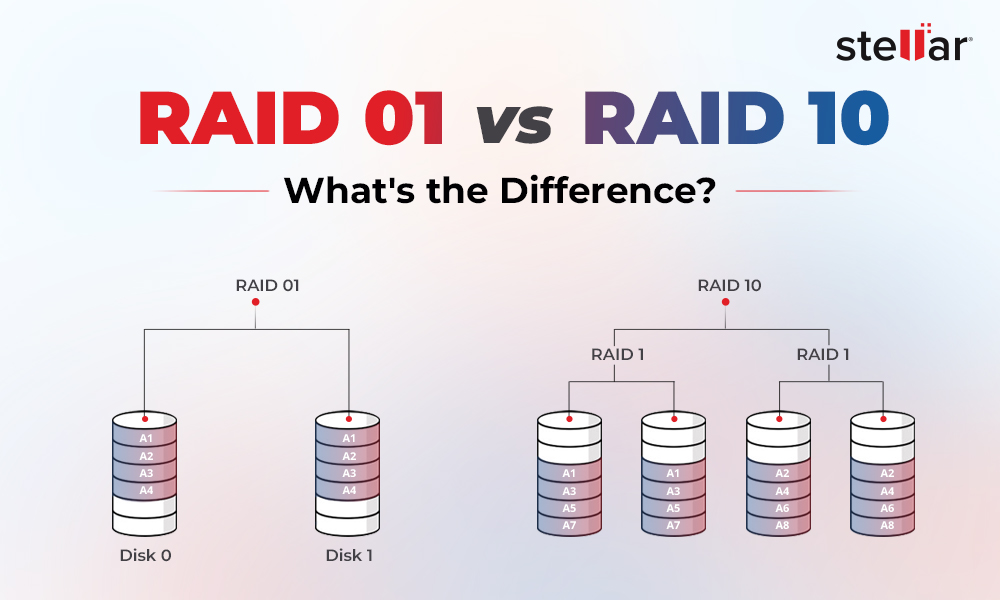
RAID 10
- Only 50% of storage is available because total storage is halved due to mirroring.
Application Performance
Different applications and software on your system have different requirements. Some applications are light on I/O (input/output) needs while others may require faster speed. Keeping this in mind, you must choose a RAID level matching your workload.
RAID 0
- It has high read and write performance because there is no RAID overhead.
- It is suited to store and access non-critical data.
- It is suitable for video/audio post-production, gaming, multimedia imaging, data logging, and CAD.
RAID 1
- Since it uses the mirroring method, it offers better read performance.
- It is ideal for mission-critical data, which requires minimal risk of loss, such as accounting, etc.
- It is suitable for small servers like web or home, with only two disks.
RAID 5
- RAID 5 read performance is comparable to that of RAID 0, but its write performance is less because it has to write parity information.
- It is suitable for file servers, backup servers, and general storage servers, streaming data.
RAID 6
- RAID 6 read performance is comparable to RAID 0, but write performance is slower because of the dual parity needs.
- It is ideal for large critical databases or transaction servers.
- It is also suitable for archiving and high availability solutions.
RAID 10
- RAID 10 has the same write performance as RAID 0 but the read performance is almost double because data is written twice.
- It is ideal for highly utilized database servers.
Redundancy (Reliability)
Data redundancy is an important factor when choosing RAID. You must ensure that you choose the RAID level that offers data protection and less downtime. Even if you are maintaining constant data backups, it's wise to choose the RAID configuration that offers data protection.
RAID 0
- RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance or data protection at all.
RAID 1
- It provides redundancy and fault tolerance, since it uses mirroring method in which the same data is stored on more than one disk.
RAID 5
- It can withstand fault tolerance up to one drive failure in the array by using block-level striping with distributed parity.
RAID 6
- It can withstand fault tolerance up to two drives failure in the array as it uses striping with double parity.
RAID 10
- It can withstand fault tolerance up to two drives failure from one side as it uses striping with the mirroring method.
Cost
Another important factor to consider while choosing the RAID level is the cost. If you want superior performance and better capacity, you might have to shell out more money.
RAID 0
- It is the most cost-effective RAID configuration from a performance and capacity standpoint. It offers maximum performance with no RAID overhead.
RAID 1
- It offers better data protection by mirroring data between two identical sets of disks. However, because of this, you need more disks than your usable capacity.
RAID 5
- Since it uses striping with distributed parity across all disks, no extra disks are occupied with mirroring, making RAID 5 cost-effective. RAID 5 is a good balance of storage, efficiency, and performance.
RAID 6
- RAID 6 is expensive because of the two extra disks required for parity.
RAID 10
- Since it is a nested RAID, i.e., the combination of two RAID levels, it is quite expensive than others.
Conclusion
Choosing the best RAID level is not an easy task. Being a home user, you can consider the factors discussed in this article while choosing a RAID level. You need to consider how fast you access the data on RAID and how much data you want to store. For example, if your main purpose is read/write performance, then RAID 0 is best for you. However, if you need data redundancy and performance, RAID 10 is a suitable option.
No matter which RAID level you choose, always remember there are chances that your RAID array or disk may fail. In such situations, keep a RAID recovery software such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician handy. It can rebuild RAID and recover data from broken, corrupt, damaged, and failed RAID 0, 5, and 6 arrays.













 6 min read
6 min read