Outlook rules make email management easy. They help automate certain actions, such as moving emails to a specific folder, flagging specific emails or messages, and setting up alerts. You can also use rules to sort, mark, and filter incoming emails. However, sometimes, you find that Outlook rules are not working when new messages arrive and the incoming emails are not going into their designated folders according to the set rules. Instead, they arrive in the root Inbox or a different folder. This issue can arise due to various factors or reasons. In this article, we will find out why the Outlook rules are not working and how to fix the issue.
Reasons for the Outlook Rules are not Working Issue
You may face issues with Outlook rules due to various reasons, such as:
- Rules are disabled.
- Rules are conflicting, overlapping, and contradicting each other.
- Corrupt or damaged rules.
- Usage of RegEx in Outlook rules.
- Rules limit is exceeded.
- Wrong rule configuration or missing conditions.
- Bugs or software-related issues.
- Outdated Outlook version.
- Corruption in the Outlook data file (PST).
Solutions to Fix the Outlook Rules are Not Working Problem
If your Outlook rules are not working properly, you can follow the solutions mentioned below to troubleshoot and resolve the problem.
1. Check if Rules are Enabled
Outlook rules are automatically enabled when you create them. However, it is advisable to confirm their status to ensure they have not been inadvertently disabled. To verify this, follow these steps:
- Open Outlook, go to File, and click on Manage Rules and Alerts.
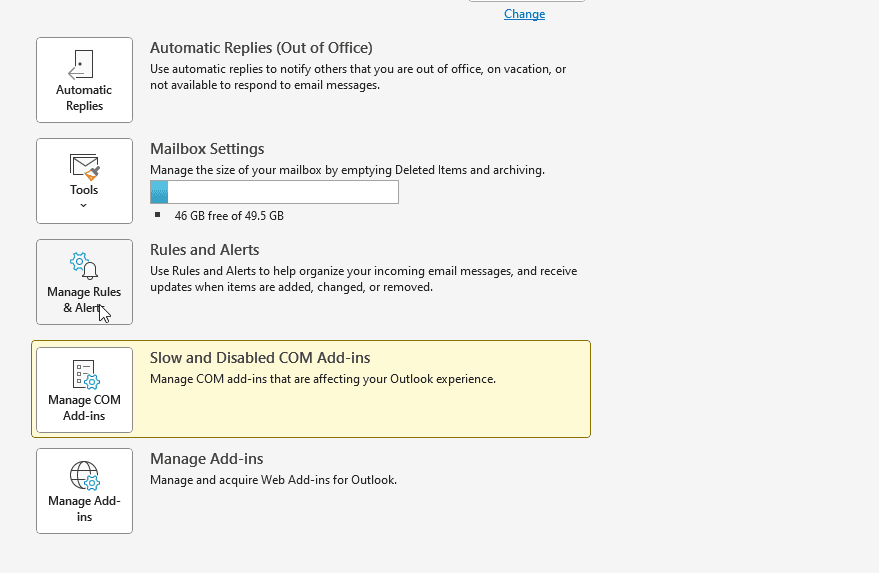
- In the Rules and Alerts dialog box, check that the checkboxes against the concerned rules are checked or ticked. If not, enable them.
- Once enabled, click Apply and then click OK.
Now, the Outlook rules that were not working should start working.
2. Check if Rules Refer to a Deleted Folder
If all the Outlook rules are enabled and still not working, then there are chances that the rules may be referring to a deleted mailbox folder or a folder that is not available in your mailbox. In such cases, Outlook may fail to execute the rules. To resolve this issue, you can review the rules and verify their dependencies using the steps mentioned below:
- Navigate to File > Manage Rules and Alerts and double-click on the Outlook rule that is not working.
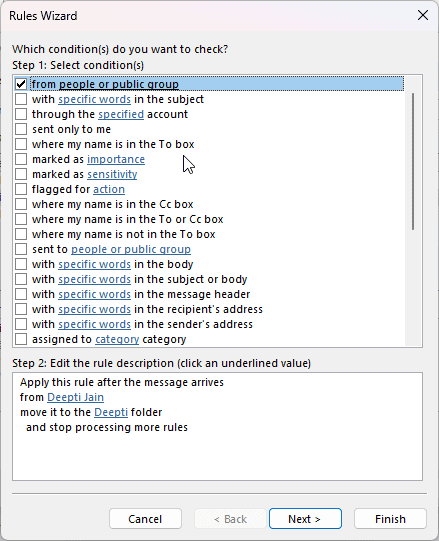
- In the Rules Wizard dialog box, click Next.
- Under Select Actions, check the rules description. Here, you will find details where or to which folder the email is being moved.
- If that folder is no longer available, you can create it or simply edit the rule by clicking on the destination folder and choosing a different or desired folder.
- Click OK.
3. Update Outlook
Latest Outlook updates often include important fixes and enhancements to ensure proper functionality of the application. Outlook rules may stop working if your application version is outdated. So, check and install any available updates by following these steps:
- Open Outlook.
- Go to File > Office Account (or Account in some versions).
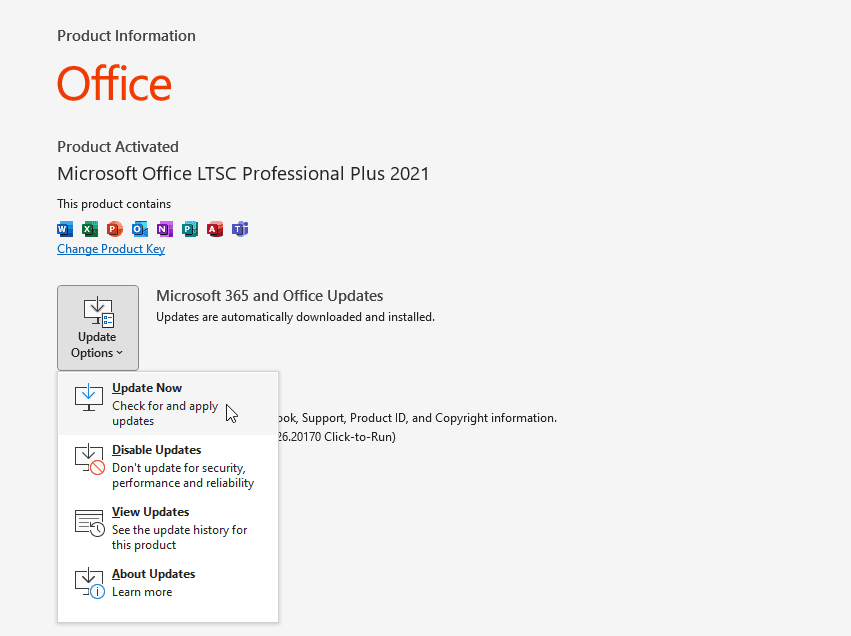
- Under Product Information, select Update Options and then click Update Now.
If the Update Now option is not available in your Outlook client, you can download and install Windows Updates to get the latest bug fixes and updates for MS Office, including Outlook.
4. Disable Add-Ins
Faulty or conflicting add-ins may also prevent the execution of rules in Outlook. You can check and remove the faulty add-ins. Close Outlook and follow the below steps:
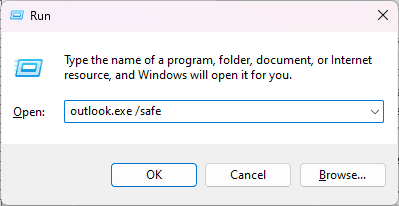
- While holding the Shift key, double-click on Outlook to launch it in safe mode. Alternatively, you can press Windows + R, type outlook.exe /safe and press Enter to start Outlook in safe mode.
- Then, click File > Options and select Add-ins.
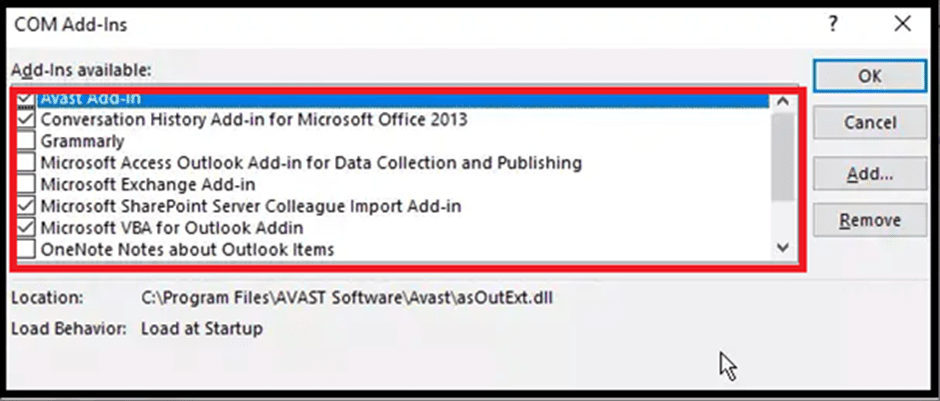
- Click the Go button and uncheck all the add-ins.
- Click OK to disable all the add-ins.
- Once the add-ins are disabled, restart Outlook normally.
5. Disable the Rules with RegEx
Regular Expressions (RegEx) are complex combinations of words and special characters used to search and match text patterns, like email addresses or specific phrases. However, RegEx is not supported in Outlook rules. Outlook’s built-in rules only offer basic filtering options, like specific words, sender addresses, or dates. If you or your administrator has added custom RegEx to your Outlook through VBA scripting, it may cause conflicts or prevent rules from executing. To check if RegEx is being used in your Outlook rules,
- Open Outlook and press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor.
- Look for any VBA scripts in the Modules or ThisOutlookSession section.
- Check if there are any rules that include pattern matching or complex conditions, such as rules that search for specific combinations of numbers, email addresses, or phrases using patterns like \d+ (for numbers) or ^[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,}$ (for email addresses).
If there are any such scripts, disable them. Then, check if rules are functioning normally in Outlook.
6. Recreate the SRS File
The Send/Receive Settings (SRS) file in Outlook contains configuration settings for sending and receiving emails for your profile. Corruption in the SRS file can also prevent Outlook from executing the rules. In this scenario, you can reset the SRS file to make the rules work properly. You can do this by following these steps:
- Close Outlook.
- Press the Windows + R keys, type %appdata%\Microsoft\Outlook and click OK or press the Enter key. Alternatively, you can navigate to the following location using the File Explorer: C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
- You will find a file named Outlook.srs. Rename this file as Outlook.srs.old. This will create a backup of the SRS file.
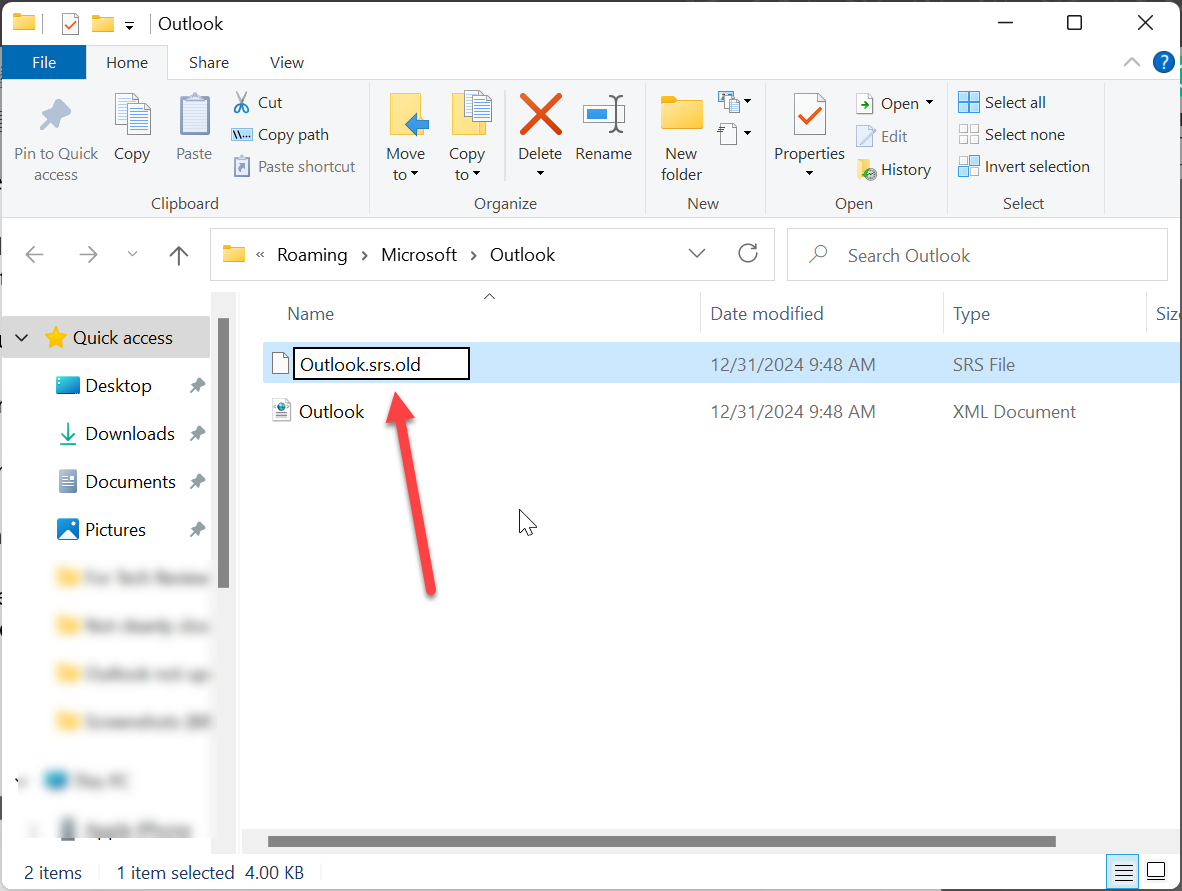
- After the backup, start Outlook. Since Outlook won’t find the SRS file as it is renamed, it will recreate a new SRS file.
Now, check if the Outlook rules are working properly.
7. Reduce the Space Used by Rules
When you create a rule in Outlook, it occupies some space in your mailbox. In Outlook desktop app, the maximum size limit for all rules in total is 256 KB. If the quota limit is already 256 KB, then you may face issues with the rules. In this case, you can reduce the space taken by the rules. The amount of space used by Outlook rules depends on factors such as the number of conditions created in a rule, the length of rule name, etc. You can reduce the space taken up by the rules by:
- Deleting old rules that are no longer needed.
- Renaming rules, having long and complicated names, with shorter names.
- Merging similar rules.
8. Delete and Recreate the Rules
If Outlook rules are not functioning as expected, it is possible that they have become corrupted. In this case, you can delete the rules and recreate them by using the following steps:
- Close Outlook and go to the Start Menu.
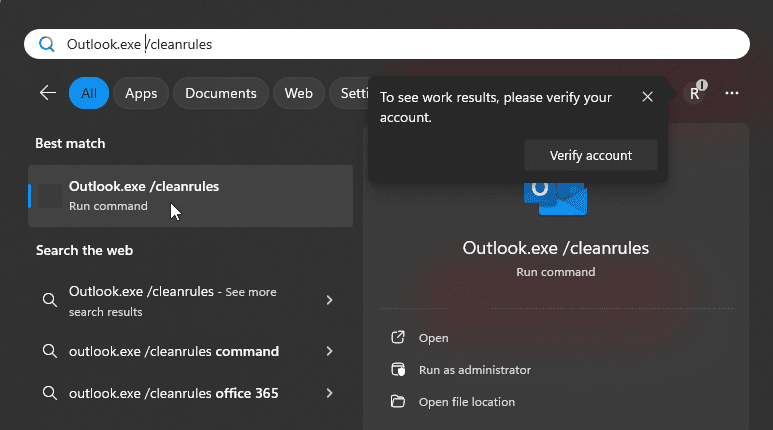
- Enter Outlook.exe /cleanrules in the search field and wait for the system to perform the search.
- Once your system found the Outlook.exe /cleanrules command-line switch, click on it or press the Enter key. You can also click Open or Run as administrator to delete all rules from Outlook.
- Now, recreate the rules in Outlook by using the Rules Wizard.
If you can’t run the outlook.exe /cleanrules, you can follow these steps to delete the rules:
- Press Windows+R and paste or type outlook.exe /cleanrules and press the Enter key or click OK.
- This will clean all the rules from Outlook.
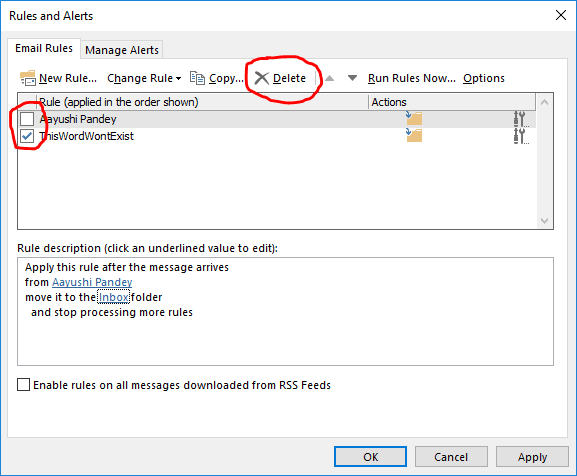
If some of the rules are not working, then you can delete only those rules, instead of all the rules. For this, follow these steps:
- Open Outlook and click File.
- Click Manage Rules & Alerts to open the Rules and Alerts dialog box.
- Select the rules you want to delete and click Delete.
Conclusion
In Microsoft Outlook, rules help you manage your emails more effectively by allowing you to set specific conditions to move, filter, and flag your emails. However, Outlook rules might sometimes fail to function properly. If your Outlook rules are not working, you can follow the methods and workarounds listed above to resolve the problem.















 8 min read
8 min read