In older versions of Exchange Server, like 2007 and 2010, the Hub Transport Service is used to take care of anything related to SMTP. In newer versions of Exchange Server (2016 and 2019), there are two services for this purpose.
- Front-End Transport Service: This is the service that other SMTP hosts used to connect to, when delivering emails to the Exchange Server. This service listens on the port 25. It can be easily identified with the name - Default Frontend \name of="" server="" /name .
- Hub Transport Service: This is the back-end service which is used by the Front-End Transport and other Exchange Server Hub Transport services. The service listens on port 2525. It can be identified as Default /name of="" server="" /name>in the Exchange Admin Center (EAC).
How to View the Connectors?
To view the connectors, follow these steps:
- Open the Exchange Admin Center (EAC).
- Click on Mail Flow.
- Click on Receive Connectors.
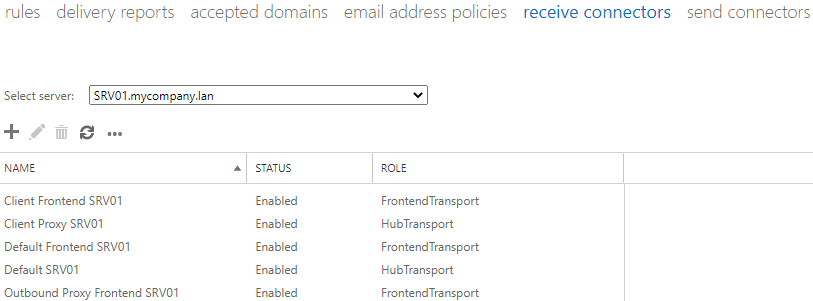
Here you can find the mentioned receive connectors.
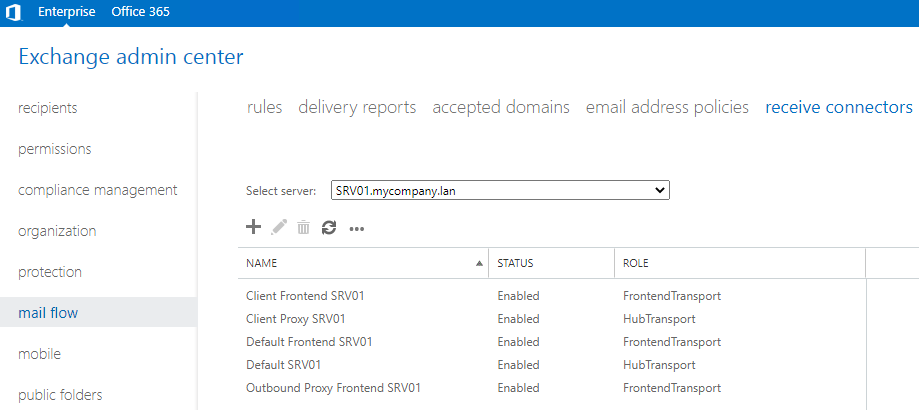 M
MIf there are connectors already created, you can still create new ones to allow other devices to send emails, like server notifications. You can also create connectors to allow other servers to relay through the local Exchange Server, like in a hybrid setup or other external devices.
How to Create Relay Connectors?
Before starting, you must be careful to not open the transport service to anyone outside as it could be easily spammed and abused by non-invited guests. So, when setting up new connectors, make sure that you limit its use to either an IP range or particular IP addresses. If this is not set, you will end up with ‘Open Relay’, where anyone can send emails from. Your public IP address could be blacklisted and abused. So, you need to be careful when setting this up.
You can create a relay connection in two different ways.
- You can create a connector which will be on the Front-End Transport. It can be restricted to IP addresses where any sending host will be treated as anonymous, and the anti-spam and message restrictions apply.
- You can create a connector on the Front-End transport, with the same restriction. However, you can add the Exchange Servers and externally secured authentication mechanisms in the connector. In this type of connector, the sending host is considered as authenticated and legit. So, emails are exempted from anti-spam and message size limitations.
Use PowerShell to Create Connectors
To create a receive connector using the Exchange Management Shell (EMS), you can use the New-ReceiveConnector command as given below.
New-ReceiveConnector -Name \relay name=""-Server \server name="" -TransportRole FrontendTransport -Custom -Bindings 0.0.0.0:25 -RemoteIpRanges /remote ip="" /remote>
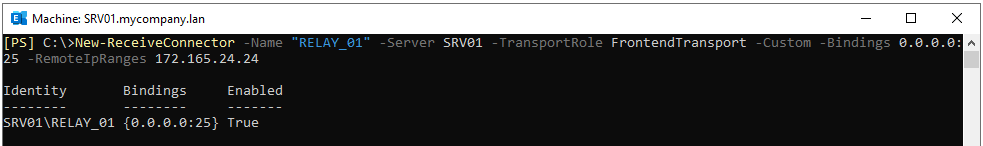
The next step is to set the permission groups and authentication mechanisms. For this, use the Set-ReceiveConnector PowerShell command as given below.
Set-ReceiveConnector " \server name="" \relay name="" -authmechanism="" externalauthoritative="" -permissiongroups="" exchangeservers<="" relay=""

Once this is done, you can verify the connector settings by using the Get-ReceiveConnector PowerShell command (as given below). This will give all the details of the created connector.
Get-ReceiveConnector -Identity \relay name="" | FL
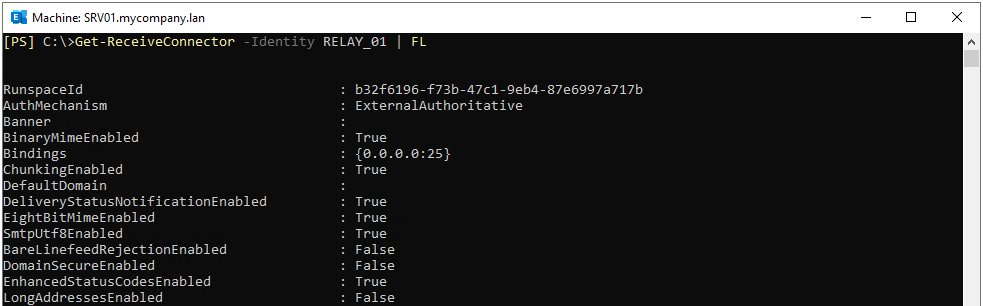
Use Exchange Admin Center (EAC)
You can also use the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) to create connectors. Follow these steps:
- Open the Exchange Admin Center (EAC), log in without administrative user, and click on mail flow from the left pane.
- Click on Receive Connectors.
- Click on the plus (+) button to create a new connector.
- Enter the name of the connector.
- Tick Frontend Transport and click Next.
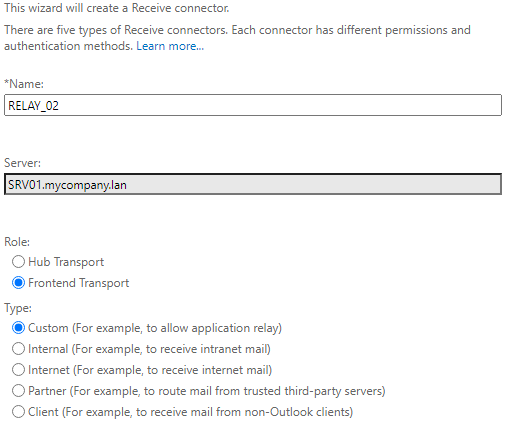
- Click Next
- You can leave the bindings as it is. It can automatically pass through any adapter of the server.
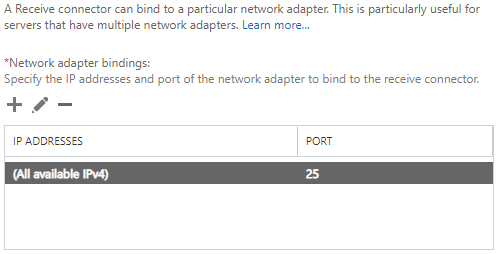
- Click Next, Now, enter the subnet or IP addresses to accept connections from. You need to put in the remote addresses in this screen.
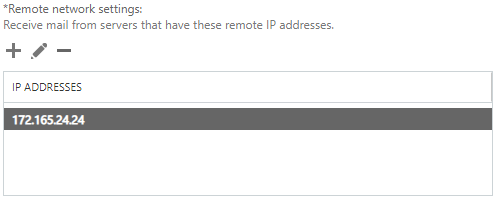
- Click Finish, Once the connector is created, highlight the connector and click on the edit
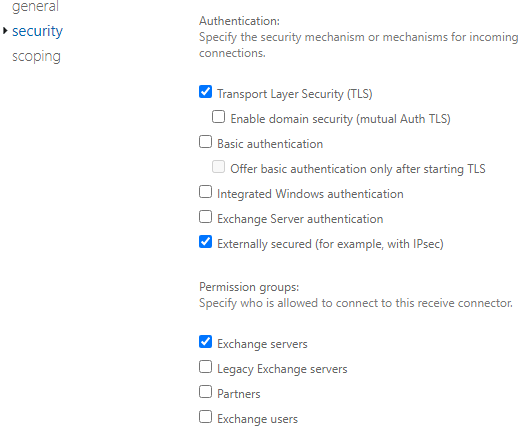
- Click on the security tab and select the Exchange Server and Externally Secured (for example, with IPsec). This is to match the example we did. However, depending on the connector’s requirements, these can be changed.
- Once ready, click on the Save
Conclusion
Above, we have discussed how to create connectors using PowerShell and the Exchange Admin Center (EAC). Since you are playing with the server’s configuration, you must ensure that no configuration would cause issues with communication between Exchange Servers, and internal mail flow.
Once you have created SMTP relay connectors, the next step is to create user profiles and mailboxes on the new Exchange Server. You also need to grant users the necessary permissions to sign in and access their email accounts for sending and receiving messages. To migrate mailboxes quickly and efficiently to the new server, you can use a specialized Exchange migration tool such as Stellar Migrator for Exchange.
Stellar Migrator for Exchange allows you to seamlessly migrate mailboxes from one Exchange Server to another or to Office 365. It supports automatic mailbox mapping and parallel migration to speed up the process. The software enables migration of all mailbox types—including user mailboxes, archive mailboxes, shared mailboxes, disabled mailboxes, and public folders—with complete data integrity. It’s designed to handle large-scale migrations with minimal downtime and zero data loss.













 6 min read
6 min read
-1848.jpg)






